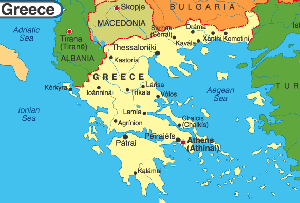
Athens – Not long ago Leonidas Hamodrakas, a lawyer in Athens, decided to pay closer attention to his family’s land holdings – some fields, a scattering of buildings and a massive stone tower – in Mani, a rural region in southern Greece.
But property ownership in Greece is often less than clear cut. So Mr. Hamodrakas put a padlock on his gate and waited to see what would happen. Soon enough, he heard from neighbors. Three of them claimed that they, too, had title to parts of the property.
In this age of satellite imagery, digital records and the instantaneous exchange of information, most of Greece’s land transaction records are still handwritten in ledgers, logged in by last names. No lot numbers. No clarity on boundaries or zoning. No obvious way to tell whether two people, or 10, have registered ownership of the same property.
As Greece tries to claw its way out of an economic crisis of historic proportions, one that has left 60 percent of young people without jobs, many experts cite the lack of a proper land registry as one of the biggest impediments to progress. It scares off foreign investors; makes it hard for the state to privatize its assets, as it has promised to do in exchange for bailout money; and makes it virtually impossible to collect property taxes.
Story courtesy of The New York Times. Click here to read more